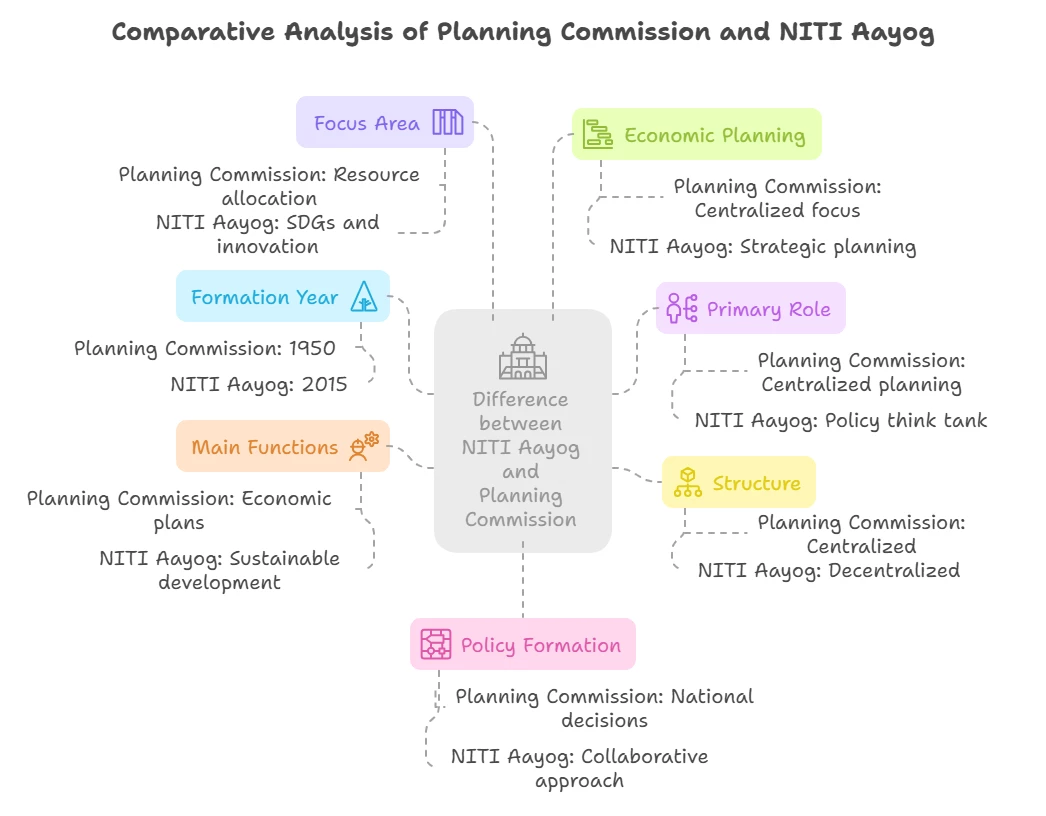
| The key difference between NITI Aayog & Planning Commission lies in their respective roles, governance structures, and objectives. NITI Aayog replaced the Planning Commission in 2015 to bring more flexibility, innovation, and cooperative federalism in India’s policy-making process. While the Planning Commission played a vital role in centralized economic planning, NITI Aayog focuses on encouraging collaborative federalism, holistic development, and strategic planning. |
General Difference between NITI Aayog and Planning Commission
A basic difference between NITI Aayog and Planning Commission is tabulated below:
Detailed Difference between NITI Aayog and Planning Commission
A detailed difference between NITI Aayog and Planning Commission is tabulated below:
NITI Aayog
NITI Aayog (National Institution for Transforming India) was created in 2015 as the successor to the Planning Commission. It was formed to foster Cooperative Federalism, encouraging states to come together for Sustainable and inclusive growth.
Furthermore, NITI Aayog continues the legacy of planning but shifts focus from Centralization to a more decentralized approach that encourages policy making through collaboration with states and union territories.
NITI Aayog’s Modernized Functions
NITI Aayog was established to promote cooperative federalism and empower states in Policy decision making. Here’s how:
- By encouraging states to actively participate in policymaking, NITI Aayog seeks to promote cooperative federalism.
- As a policy think tank, it advises the federal government as well as the states.
- The organization is essential in monitoring and assessing the Sustainable Development Goals (SDGs) advancement.
- By using innovation and strategic planning, NITI Aayog creates and executes plans that are centered on long-term national growth.
- It actively encourages entrepreneurship and propels grassroots economic change.
- To guarantee that decisions are supported by substantial evidence, the organization promotes data-driven policies.
- Because NITI Aayog promotes cooperative planning, states are free to create plans that are suited to their unique problems.
- It is also essential for developing national strategies in important areas like technology education and health.
- Through its collaborative approach, NITI Aayog assists states in creating solutions that meet their particular requirements and difficulties while also being in line with national objectives.
NITI Aayog’s Key Initiatives and Achievements
One of the Major achievements of NITI Aayog is its active role in Promoting Cooperative Federalism.
Unlike the Planning Commission, which operated on a Centralized approach, NITI Aayog works in close collaboration with state governments to ensure that state specific needs are addressed while also aligning with national objectives.
Furthermore, through Task Forces and Expert Groups, NITI Aayog helps craft policies that foster regional development and inclusivity, ensuring balanced growth across the nation.
Key Initiatives by NITI Aayog
NITI Aayog has undertaken several initiatives that have had a significant impact on India’s development Policies. These Include:
- Atal Innovation Mission (AIM): Focuses on Promoting Innovation and Entrepreneurship among the Youth of India.
- Sustainable Development Goals (SDGs): NITI Aayog tracks India’s Progress towards achieving the SDGs, integrating them into national and state-level Policies.
- Aspirational District Programme: Aimed at transforming backward districts across India by providing them with national and state level policies.
- State Investment Promotion: Encouraging state-level reforms to improve the ease of doing business and attract investments.
NITI Aayog’s Transformative Role
NITI Aayog’s role is centered around Flexibility, Cooperation, and Innovation. The goal is to establish a more dynamic and inclusive policy framework by:
- Promoting state government participation
- Decentralising Policy-Making
- Encouraging Collaborative governance between the central and state governments.
- In addition, NITI Aayog promotes entrepreneurship and technological advancements as key elements of India’s development.
- This transition from centralised planning to participatory developments marks a significant shift in India’s model.
Overall Impact on Governance
NITI Aayog’s impact on governance has been transformational. It has not only contributed to the Socio-economic development of India but also helped in improved governance structures at the state level. Furthermore, the focus had shifted from rigid directives to more adaptable, innovative solutions to challenges. The transition from Planning Commission to NITI Aayog is an essential milestone in India’s democratic evolution, ensuring that development is driven by Collaboration.
Planning Commission
The Planning Commission was established in 1950 by the government of India to formulate Five Year Plans for the Country’s economic development. It played a Central role in Managing. It played a central role in managing Economic Policies and ensuring that national resources were utilised optimally for growth. Under its leadership, India progressed through : \
- Industrialization
- Agricultural Reforms
- Infrastructural development
Planning Commission’s Impact
The Planning Commission had a profound impact on India’s governance and economic structure. It laid foundations for India’s post-independence recovery and guided the country through its Five Year Plans.
However, its Centralized Framework had limitations:
- It lacked flexibility in adapting to the evolving economic conditions.
- Its top-down approach was not suited to address local issues and state-specific challenges.
Conclusion
An important change in Indian governance was brought about by the establishment of NITI Aayog which placed a strong emphasis on innovation, federalism and sustainable development. In contrast to the centralized Planning Commission, NITI Aayog advocates for a decentralized state-inclusive strategy that addresses intricate problems like environmental degradation and economic inequality. This shift represents a shift in India's approach to policymaking from a top-down to a more inclusive and collaborative model.