The CBSE Class 12 Political Science Board Exam 2025 is scheduled to be conducted on 22nd March 2025. Political Science being a vital subject contributes heavily towards increasing overall board exam marks. To assist students with thorough preparation, this article presents the CBSE Class 12 Political Science Sample Paper 2025 by Experts with Solutions. These questions are compiled by subject experts for students to solve during final revision as all these questions importantly cover all the major topics in the syllabus.
Also check: CBSE Topper Answer Sheet 12th Political Science 2025 PDF Download
CBSE 12th Political Science Expert Sample Paper 2025 Characteristics
| Feature | Details |
| Prepared by Experts | Designed by subject specialists for accuracy. |
| Latest Syllabus & Pattern | Aligned with CBSE Class 12 Political Science (2025). |
| Important Questions | Covers key topics & expected question types. |
| Additional Questions | Extra practice beyond CBSE sample papers. |
| Includes Solutions | Well-structured answers for quick revision. |
| PDF Format | Downloadable & accessible offline. |
CBSE Class 12 Political Science Sample Paper 2025 with Answers
1. Which one of the following statements was not a feature of the Soviet System?
a) A minimum standard of living was ensured to all citizens.
b) The soviet government subsidized the basic necessities.
c) There was no unemployment.
d) People had the right to property.
2. Which trade agreement promised a free trade zone for SAARC countries?
a) South Asian Free Trade
b) Northwest America Free Trade
c) North Atlantic Free Trade Agreement
d) North America Free Trade Agreement
3. The Janata Party split and the government which was led by ______ lost its majority in less than 18
months.
a) Morarji Desai
b) Karpoori Thakur
c) J.P. Narayan
d) Rammanohar Lohia
4. Which of the following CWC stands for?
a) Chemical Weapons Convention
b) Convention on weapon of chemical
c) Carbon weapon convention
d) Convention on weapon for children
5. Assertion (A): Six- points proposal of Sheikh Mujib-ur Rehman for greater autonomy to east Pakistan.
Reason(R): India and Bangladesh sign the Farakka Treaty for sharing of the Ganga waters in 1966.
a) Both A and R are true and R is the correct explanation of A.
b) Both A and R are true but R is not the correct explanation of A.
c) A is true but R is False.
d) A is False but R is True.
6. Assertion(A): World Trade Organization is an international organisation.
Reason(R): It sets the rules for global trade.
a) Both A and R are true and R is the correct explanation of A
b) Both A and R are true but R is not the correct explanation of A.
c) A is true but R is False.
d) A is False but R is True.
7. When Anandpur Sahib Resolution was passed?
a) 1973
b) 1962
c) 1965
d) 1967
8. Arrange the following in sequence.
I. Formation of separate Andhra state
II. Nagpur session of Congress
III. Appoints State Reorganisation commission by Central Government
IV. Creation of State Maharashtra and Gujarat.
a) I, II, III and IV
b) II, I, III and IV
c) I, II, IV and III
d) III, IV, II and I
9. Name the founder President of ‘Congress Socialist Party’.
a) K.M. Munshi
b) Acharya Narendra Dev
c) Shyama Prasad Mukherjee
d) Minoo Masani
10. Bodo community belongs to_________.
a) Manipur
b) Assam
c) Mizoram
d) Arunachal Pradesh
11. Which one of the following Chinese leaders was accompanied by Dalai Lama during the visit to India in 1956.
a) Hua Guofeng
b) Zhao Ziyang
c) Premier Zhou Enlai
d) Li Peng
12. Who was the leader of the Dravidian Movement in Tamil Nadu?
a) Karunanidhi
b) C. N. Annadurai
c) E.V. Ramasami
d) M.G. Ramachandran
Section B
13. Name any two agencies of the United Nations.
14. What are the two Directive Principles of State Policy relating to foreign affairs policy?
15. What were the reasons for the dominance of Congress Party till 1967?
16. What do you mean by the non-traditional notion of security?
17. Highlight any two features of the Soviet System.
18. What were the impacts of the elections of 1989 on Indian politics?
Section C
19. Explain any two effects of globalisation on the culture of a country.
20. ‘Coalition governments proved to be a boon for democracy in India.’ Support this statement with the help of the most suitable arguments.
21. Describe the two reasons that led to National Jubilation (triumph) in India after the 1971 war with Pakistan.
22. What are the objectives of military alliances? Give an example of a functioning military alliance with its specific objectives.
23. The Assam Movement from 1979 to 1985 is the best example of the movements against ‘outsiders’. Support the statement with suitable arguments.
Section D
24. Read the passage given below and answer the questions that follow:
A new chapter of peace and cooperation might evolve in South Asia if all the countries in the region allow free trade across the borders. This is the spirit behind the idea of the SAFTA. The Agreement was signed in 2004 and came into effect on 1 January 2006. The SAFTA aims at lowering trade tariffs. But some of our neighbours fear that the SAFTA is a way for India to ‘invade’ their markets and to influence their societies and politics through commercial ventures and a commercial presence in their countries. India thinks that there are real economic benefits for all SAARC nations from the SAFTA and that a region that trades more freely will be able to cooperate better on political issues. Some critics think that the SAFTA is not worth for India as it already has bilateral agreements with Bhutan, Nepal, and Sri Lanka.
(i) What is the full form of SAFTA?
(a) South America Free Trade Agreement
(b) South Africa Free Trade Agreement
(c) South Asian Free Trade Agreement
(d) None of the above
(ii) Why was SAFTA signed?
(a) To allow free trade among the South American nations.
(b) To increase the political interference of the nations in South Asia.
(c) To allow free trade among the South Asian nations.
(d) None of the above.
(iii) Why do some of the neighbours of India fear SAFTA?
(a) India will impact their politics
(b) India will impact their commercial ventures
(c) They fear that the economic influence of India will increase
(d) All of the above
(iv) India does not have a trade agreement with which of the following nations?
(a) Pakistan
(b) Sri Lanka
(c) Nepal
(d) Bhutan
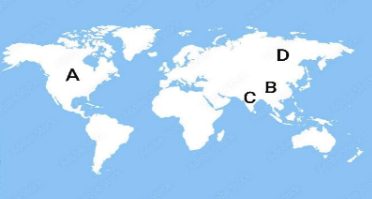
25. In the given outline political map of the world, four countries have been marked as (A), (B), (C), and (D). Identify these countries on the basis of the information given below and write their correct names in your answer book along with the respective serial numbers of the information used and the concerned alphabets as per the format that follows:
(i) A country that did a nuclear test in the year 1998.
(ii) A communist nation during the Cold War.
(iii) A capitalist country that dropped an atomic bomb on Japan.
(iv) A communist nation initially under Mao Zedong.
| Sr. No. of the information used | Alphabet Concerned | Name of the state |
| (i) | ||
| (ii) | ||
| (iii) | ||
| (iv) |
26. Study the given cartoon and answer the questions that follow:

(i) Name the person who is sitting in the centre of the cartoon.
(a) Jawaharlal Nehru
(b) Sardar Patel
(c) Morarji Desai
(d) Rajendra Prasad
(ii) Which one of the following challenges was faced by the above mentioned person?
(a) Rehabilitation of refugees
(b) Partition of India
(c) Integration of Princely States
(d) Reorganisation of states on linguistic lines
(iii)During the ______, the state boundaries were drawn on administrative convenience.
(a) Mughal rule
(b) Maratha rule
(c) British rule
(d) Portuguese rule
(iv) Name the movement which demanded linguistic reorganisation of the Madras province.
(a) Vishalandhra movement
(b) State Reorganisation movement
(c) Satyagraha movement
(d) Tamil movement
SECTION E
27. Describe the factors that make most of the former Soviet Republics prone to conflicts and threats.
OR
Highlight any three positive and three negative features each of the Soviet system in the Soviet Union.
28. Explain the role of the European Union as a supranational organisation.
OR
How did China rise to be an economic superpower? Assess.
29. Examine the grave economic crisis prior to fourth general election of 1967. Assess the electoral verdict also.
OR
Examine the main factors responsible for the rise and fall of the congress party’s dominance in India.
30. Explain the salient features of coalition governments.
OR
Explain any five elements of consensus which have emerged among most political partis after the Lok Sabha elections by 2004.
CBSE Class 12 Political Science Sample Paper 2025 Answers
| Answers |
| 1. (d) People had the right to property. |
| 2. (a) South Asian Free Trade |
| 3. (a) Morarji Desai |
| 4. (a) Chemical Weapons Convention |
| 5. (c) A is true but R is False. |
| 6. (a) Both A and R are true and R is the correct explanation of A. |
| 7. (a) 1973 |
| 8. (b) II, I, III and IV |
| 9. (b) Acharya Narendra Dev |
| 10. (b) Assam |
| 11. (c) Premier Zhou Enlai |
| 12. (c) E.V. Ramasami |
| 13. The United Nations (UN) is a global organization that works to promote peace, security, and cooperation among nations. Two key agencies of the UN are: (i) United Nations Children’s Fund (UNICEF): This agency focuses on child welfare, including education, healthcare, and nutrition, especially in developing nations. (ii) United Nations Educational, Scientific and Cultural Organization (UNESCO): It promotes international collaboration through education, science, and culture to ensure peace and security. |
| 14. What are the two Directive Principles of State Policy relating to foreign affairs policy? Directive Principles of State Policy (DPSP) are guidelines in the Indian Constitution that aim to establish social and economic democracy. Two DPSPs related to foreign affairs policy are: (i) Promotion of International Peace and Security (Article 51): The Indian government aims to maintain friendly relations with other countries and uphold global peace. (ii) Respect for International Law and Treaty Obligations: India commits to following international agreements and respecting foreign policies to maintain diplomatic relations worldwide. |
| 15. What were the reasons for the dominance of the Congress Party till 1967? From 1947 to 1967, the Indian National Congress was the dominant political party due to several reasons: (i) Strong Leadership: Leaders like Jawaharlal Nehru and Sardar Patel had mass appeal and led the country through major transitions such as independence and the integration of princely states. (ii) Lack of a Strong Opposition: Other political parties, like the Jan Sangh and Communist Party of India (CPI), were relatively weak and lacked nationwide support. (iii) Congress' Role in the Freedom Struggle: The party had a historical legacy of leading India to independence, which earned it public trust and credibility. (iv) Welfare and Development Programs: The Congress introduced several economic and social reforms, such as the Five-Year Plans, industrialization, and land reforms, which strengthened its popularity. |
| 16. What do you mean by the non-traditional notion of security? The concept of security has evolved beyond traditional military threats. The non-traditional notion of security includes threats that are not related to direct military conflicts but still pose significant risks to a country’s stability. These include: (i) Environmental Security: Issues like climate change, deforestation, and water scarcity impact human survival and economic stability. (ii) Economic Security: Ensuring financial stability, job opportunities, and fair trade policies for all citizens. (iii) Health Security: Preventing the spread of pandemics and ensuring access to medical facilities. (iv) Terrorism and Cybersecurity: Protecting nations from terrorist attacks and cyber threats that can disrupt governance and personal security. |
| 17. Highlight any two features of the Soviet System. The Soviet System, which existed in the USSR before its collapse in 1991, was based on communist ideology. Two key features of the system were: (i) State Ownership of Resources: The government controlled industries, land, and businesses, ensuring no private property or capitalist economy. (ii) A Centrally Planned Economy: The Soviet government made all economic decisions, including production, pricing, and distribution, through Five-Year Plans to ensure equal wealth distribution. |
| 18. What were the impacts of the elections of 1989 on Indian politics? The 1989 general elections marked a turning point in Indian politics due to the following reasons: (i) End of Single-Party Dominance: The Congress party lost its absolute majority for the first time, paving the way for coalition politics. (ii) Rise of Regional and Caste-Based Parties: Parties like Janata Dal, Samajwadi Party, and Bahujan Samaj Party (BSP) gained political significance by focusing on caste-based and regional issues. (iii) Shift to Coalition Governments: This period marked the beginning of coalition rule, where multiple parties had to work together to form a government. (iv) Growth of Hindutva Politics: The BJP emerged as a strong contender by promoting the Ram Janmabhoomi movement, influencing future political landscapes. |
| 19. Explain any two effects of globalization on the culture of a country. Globalization has led to the increased exchange of ideas, traditions, and lifestyles among different nations. Two major effects on culture are: (i) Cultural Homogenization: Due to the influence of Western culture through media, fashion, and technology, many countries have started adopting a globalized lifestyle. For example, the widespread popularity of McDonald's, Hollywood movies, and Western fashion trends. (ii) Revival of Local Cultures: While globalization spreads dominant cultures, it has also encouraged countries to preserve their own heritage. Many nations have started promoting traditional festivals, cuisine, and art forms to maintain their unique identity. |
| 20. ‘Coalition governments proved to be a boon for democracy in India.’ Support this statement with the help of the most suitable arguments. Coalition governments occur when multiple political parties come together to form a ruling government. They have been beneficial for Indian democracy in the following ways: (i) Wider Representation: Regional and smaller parties get an opportunity to influence national policies, ensuring better representation of diverse communities. (ii) Consensus-Based Decision-Making: Since no single party has absolute control, policies are formulated after discussion and agreement, leading to more balanced and inclusive governance. (iii) Greater Accountability: Coalition governments are often more accountable as they depend on multiple parties, reducing the chances of autocratic rule. |
| 21. Describe the two reasons that led to National Jubilation in India after the 1971 war with Pakistan. The 1971 Indo-Pak war was a major event in India's history, leading to great national pride due to: (i) Creation of Bangladesh: India’s military victory led to the liberation of East Pakistan (now Bangladesh), showcasing India's power and commitment to humanitarian efforts. (ii) Strengthening of India’s Global Image: India emerged as a strong regional power, gaining international recognition for its military strategy and diplomatic skills. |
| 22. What are the objectives of military alliances? Give an example of a functioning military alliance with its specific objectives. Military alliances are formed between countries to enhance security and defense cooperation. Their main objectives include: (i) Collective Defense: Member nations pledge to defend each other in case of external aggression. (ii) Strategic Partnership: Countries share military resources, intelligence, and technology for enhanced security. Example: North Atlantic Treaty Organization (NATO) – Established in 1949, NATO ensures mutual defense among its member countries against external threats, primarily aimed at deterring aggression from adversaries |
| 23. The Assam Movement from 1979 to 1985 is the best example of the movements against ‘outsiders’. Support the statement with suitable arguments. The Assam Movement (1979-1985) was a significant protest led by the All Assam Students’ Union (AASU) against illegal immigrants from Bangladesh. Reasons why it is considered the best example of movements against outsiders: (i) Protest Against Illegal Migration: Assamese people feared that illegal migration from Bangladesh would change the demographic and cultural identity of Assam. (ii) Resulted in the Assam Accord (1985): The movement led to an agreement where the Indian government promised to detect and deport illegal immigrants while granting special protections to the Assamese people. |
Also check: CBSE Class 12 Political Science Top 50 MCQs to Score Highly!
